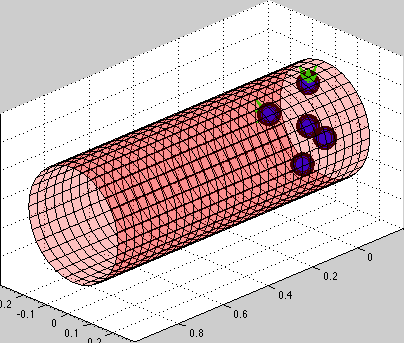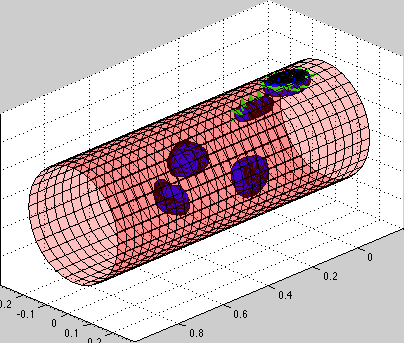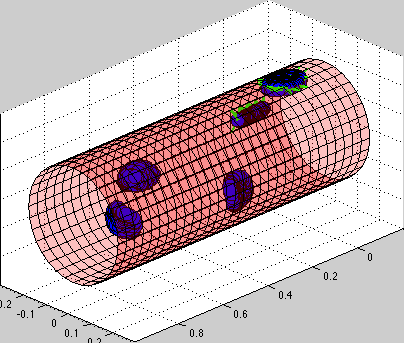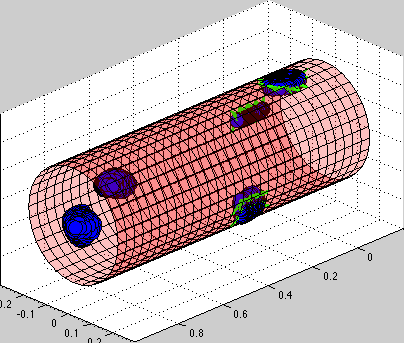
Circulating tumor cells transported through the blood vessel
 |
Goals:
Use the biomechanical model to investigate how circulating tumor cells are transported through the blood vessel, and what are the required conditions for tumor cell attachment to the vessel wall.
Mathematical Model: A classical fluid-structure interaction technique called the Immersed Boundary Method was used to model interactions between the cell and the blood flow inside the vessel during cell transport. Computational tools:i The model is coded using the Matlab system, and all images and movies are made also using the Matlab system. Author: Kasia Rejniak: labpages.moffitt.org/rejniakk |
| Simulation movie: this simulation presents several circulating tumor cells carried with the blood flow inside the vessel. Some of the cells come close to the vessel wall and initiate cell-vessel wall adhesion. The walls of the bllod vessel are build from stiff springs [red]. The cell cortex is build from linear Hookean springs [blue]. Cell adhesions to vessel walls are also modeled as springs [green]. Note the dynamical rearrangement of adhesion forces (new adhesions are formed on teh cell front, while adhesions on the cell tail get removed). |